As more and more spine surgeries are performed annually, it is our mission to help surgeons treat their patients better. Today many spine surgeons are already experiencing the confidence and precision that comes with performing complex spine cases in Philips cutting edge Hybrid OR. Now we are on a research journey to further innovate intra-operative navigation for complex open and minimally-invasive spine surgeries with our new Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation technology.
Why push the limitations of navigation for complex spine procedures?
Our Spine suite solution with XperCT cone-beam CT and large field-of-view 2D and 3D images is a perfect example, which offers remarkably detailed insights during each phase of a spine procedure. Building on that strong base and our intensive collaborations with medical professionals at the forefront of spine procedures, we are aiming to take image guidance technology to the next level of precision. Our latest advance opens up new possibilities in performing open and minimally-invasive spine procedures by bringing imaging and Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation together in one solution.
How does Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation work?
Combines 3D X-ray imaging and optical imaging in a unique augmented-reality view of the inside and outside of a patient
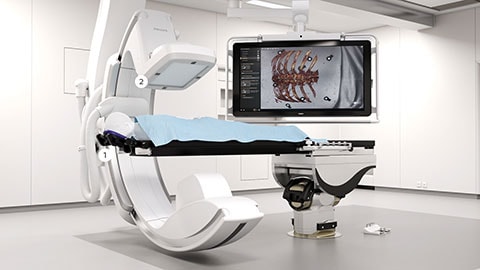
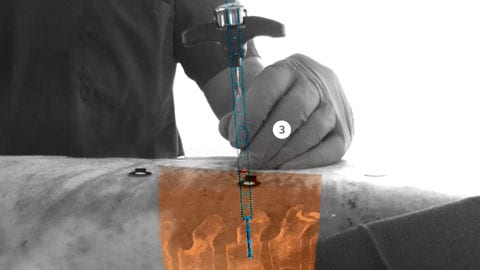
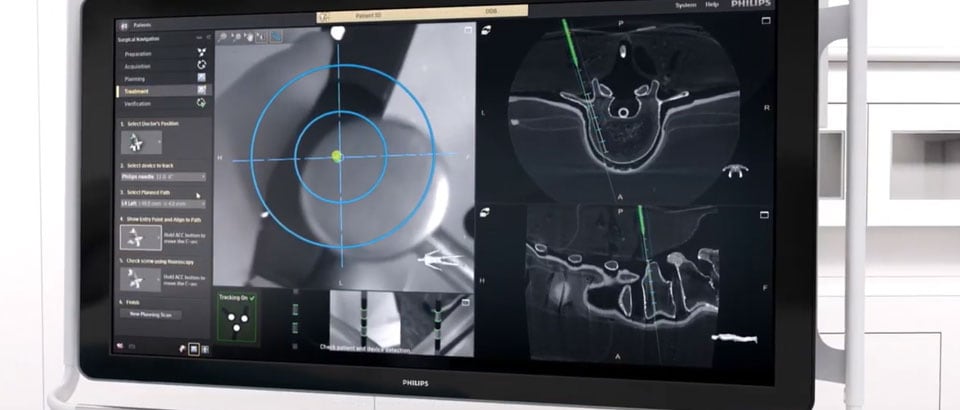
Our new Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation technology is being developed to add additional capabilities to manage X-ray dose (1 in picture above). The technology uses high-resolution optical cameras integrated in the flat panel X-ray detector (2) to image the surface of the patient. It then combines the external view captured by the cameras, and the internal 3D view of the patient acquired by the X-ray system, to construct a 3D augmented-reality view of the patient’s external and internal anatomy (3). This real-time 3D view of the patient’s spine in relation to the planned path, aims to improve procedure planning, surgical tool navigation and implant accuracy, as well as reduce procedure times. The Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation technology has the following characteristics:
First Clinical Investigation results using Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation Technology

The primary objective of this clinical investigation is to estimate the accuracy of pedicle screw placement using Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation Investigational Device

Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm in Sweden is the first in a series of global clinical studies

20 Patients treated, of which 13 with Scoliosis
253 screws placed with Surgical Navigation

94% screw placement accuracy in difficult Spine deformity surgeries

5 min Average screw placement time 50% below 4 minutes

Zero Device-related adverse events
Zero X-ray during navigation
Related pre-clinical publications
Augmented Reality on a C-arm system: A Preclinical Assessment for Percutaneous Needle Localization
Surgical Navigation Technology Based on Augmented Reality and Integrated 3D Intraoperative Imaging A Spine Cadaveric Feasibility and Accuracy Study
Feasibility and Accuracy of Thoracolumbar Minimally Invasive Pedicle Screw Placement With Augmented Reality Navigation Technology
Radiation dose and image quality comparison during spine surgery with two different, intraoperative 3D imaging navigation systems
Machine learning for automated 3-dimensional segmentation of the spine and suggested placement of pedicle screws based on intraoperative cone-beam computer tomography
Want to know more? For complimentary information, please do not hesitate to reach-out to: Disclaimer: Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation is not yet available for delivery. Not CE-marked and not available in the USA.