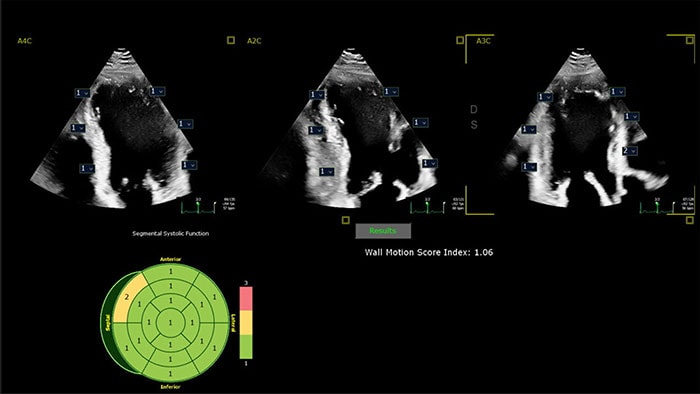
Greater patient comfort and enhanced diagnostic confidence The new ePatch-based service allows for a longer period of continuous recording and prolonged insights into a patient’s health condition. The ePatch comes as a ‘ready-to-go’ unit. A cardiologist or nurse applies the device to the patient’s sternum, located in the center of the chest, during a visit to the doctor’s office. It is comfortable and splash-proof and can even be worn in a shower, allowing patients to maintain their daily routines, including sports activities. The device’s sensor continuously records and stores the patient's heart activity day and night for up to 14 days. The recorded data is then retrieved and analyzed by AI-based software that searches for irregularities that indicate heart arrhythmias and makes an automatically generated concept report with findings for the clinical teams to evaluate further. Previously, patients had to use conventional Holter monitors that required up to seven to ten ECG electrodes to be applied to the patient's chest, linked to a bulky control unit worn on a belt or necklace. These bulkier Holter monitors typically limit patients’ ability to go about their normal daily activities, which could impact diagnostic yield. With traditional Holter monitors, the application process, data analysis and reporting, and cleaning process afterward can be labor-intensive and inefficient for clinical staff. Additionally, a traditional Holter monitor is also relatively costly, which could often limit their availability, causing patients to wait longer for their tests, and they typically only allow 72 hours of continuous wearing and recording. “With the longer recording capability of the ePatch, we have a higher chance of detecting an arrhythmia,” said Alexandra Bevers, heart function lab technician and Holter analyst at the Martini Hospital. “Because the patch is a single device that adheres well to the patient’s chest, compared to our traditional Holter with 7 leads, this results in minimal interference and a more reliable recording, allowing ECG analysts like me to evaluate the data quite quickly and provide the cardiologists with the information needed to support a diagnosis.” 56-year-old stroke patient exemplifies the program's impact Marco: “After my stroke, I had been monitored in the hospital for 24 hours twice before. Nothing was found during those times. I am relieved that something has now been discovered that the clinical team believes has been causing my problems and can be prevented with the right medication.” Beyond enhancing patient experiences and diagnoses, the hospital's cardiology department aims to significantly alleviate the growing workload on its staff through this program while also driving cost efficiencies.
Marco, a 56-year-old patient recovering from a stroke, exemplifies the program's impact. His Philips ePatch identified atrial fibrillation on the fifth day of his monitoring program, shedding important light on the potential cause of his initial stroke. Utilizing the insights provided by the ePatch, his clinical team has been able to provide Marco with a proactive personalized treatment to help avert future heart or stroke problems.
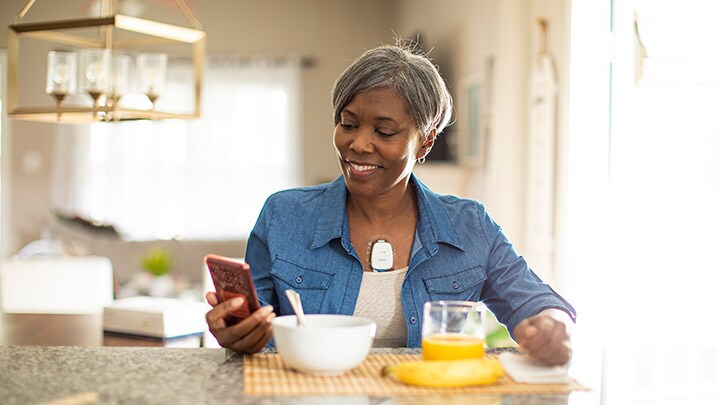

Building on years of success in the U.S. The introduction of this initiative in the Netherlands is built on years of successful experience in the United States, where yearly more than 1.2 million patients are being monitored using comparable Philips wearable e-patches and remote telemetry programs. These programs have demonstrated heightened atrial fibrillation detection and major cost savings per patient. To learn more about Philips’ broad portfolio of ECG solutions, visit the Gobio website. [1] New post-cryptogenic stroke remote telemetry study demonstrates increased atrial fibrillation detection and USD 4 million in cost savings using initial Philips BioTel Heart MCOT monitoring
[2] Heart.org